The Interventional Neuroradiology Unit aims to diagnose and treat vascular diseases of the Central Nervous System through the method of endovascular access and restoration, and by using this type of treatment, avoiding “open surgery”.
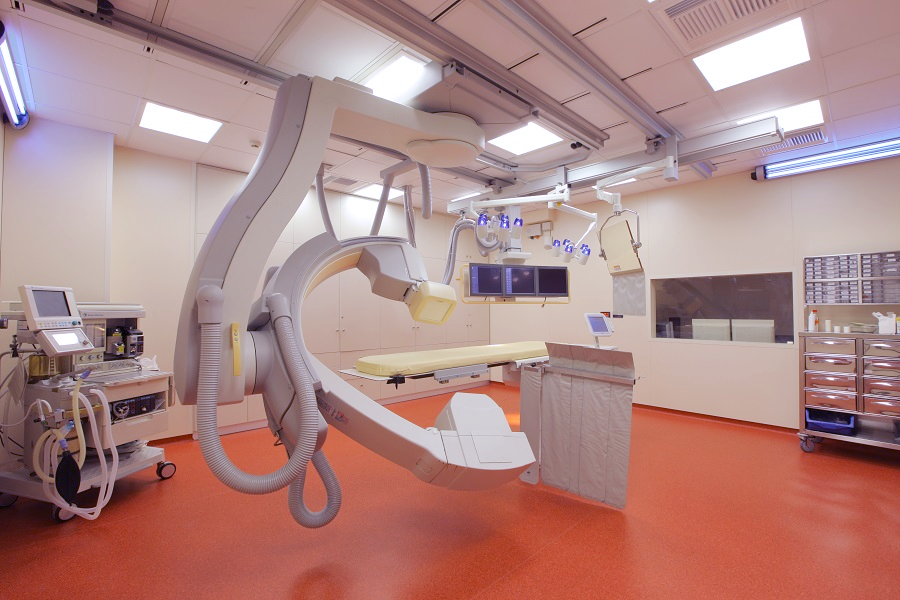
The Unit is equipped with the modern and advanced technology of the Angiographic Suite Philips Allura X-Per FD 20, which includes a Flat Detector and XPer Angio technology, and which specializes in neuroradiology applications which create three-dimensional 3D-RA Angiography and three-dimensional Digital Intravascular Navigation and can also perform CT – Computed Tomography and Stereotactic Surgeries.
Interventional Neuroradiology Applications
Diagnostic, intra-arterial digital subtraction angiographies are used for diagnosing diseases of the cervical vessels, brain and spinal cord.
The diagnostic approach for vascular diseases of the Central Nervous System is initially conducted using modern imaging methods, such as CT scans and MRI.
The diagnostic process is completed, where necessary, by conducting intra-arterial digital subtraction angiography, which constitutes the most detailed and comprehensive diagnostic method and parameterization of vascular diseases, as well as the study of their hemodynamic characteristics.
Treatment of cerebral aneurisms by embolization
Cerebral aneurism is a localized dilation of the wall of a vein, usually in arterial bifurcation points on their subarachnoid route. Brain aneurysms can crack and cause subarachnoid hemorrhage. The neurosurgical method of dealing with them suggests the selective endovascular exclusion of the aneurysmal sac, by inserting removable coils, avoiding in this way the opening of the skull. Furthermore, in combination with the use of special distending catheters (balloons) and stents, the mother vessel is protected from the protrusion of coils, ensuring excellent results.
Treatment of arteriovenous malformations and restoration of the natural flow by embolization
Arteriovenous malformations are abnormal communications between nutrient artery branches and cerebral veins. Within these abnormal arteriovenous networks, heavy flows through the communication points are observed, as well as morphological abnormalities, which may cause bleeding in the central nervous system. The endovascular treatment of malformations, made by selective catheter placement in the nutrient artery branches using microcatheters and the administration, through them, of liquid embolic material, aims at achieving the ideal result of the complete exclusion of dysplasia. This technique can be used in combination with other treatments such as surgical intervention and stereotactic radiosurgery (c-Knife), where necessary, depending on the size, location and the neuroarchitecture of the communication paths.
Intraluminal restoration of vascular stenoses in the neck and intracranial vessels, by using angioplasty and placement of a stent
Atherosclerosis, with attendant disruption of the endothelium, or arterial stenosis, is the most frequent cause of stenosis of the carotid artery, the vertebral arteries and other intracranial vessels. Stenosis and subsequent blockage of blood vessels in the cervical and intracranial vessels is the common reference point in the pathogenesis of most cerebral infarctions. Interventional Neuroradiology, through intraluminal treatment, performs an opening of the stenosed vessel through angioplasty by placing specialized dilated catheters (balloons) and positioning metal stents.
Treatment of acute ischemic stroke, by pharmaceutical thrombolytic therapy and mechanical clot withdrawal
The ischemic stroke episode is the first cause of disability, the second cause of dementia and death, and the major cause of serious neurological problems. Atherosclerosis, with attendant disruption of the endothelium, or the narrowing of the lumen of the artery is a frequent cause of ischemic stroke especially in the elderly. The treatment of an acute ischemic episode is done by administering specific thrombolytic drugs, either intravenous or intra-arterial, through selective catheterization of the affected vessel. As well as by mechanical clot withdrawal, using specialized neurosurgical systems. It is of catalytic importance, for the early restoration of cerebral blood flow and improvement of the installed neurological system, that the problem has been quickly identified, the patient has been hastily transferred to the hospital, and thrombolytic therapy has been urgently administered.
Preoperative embolization of vascularized tumors, aiming to reduce intraoperative blood loss during the removal of the tumor
The preoperative embolization of vascularized tumors is intended to reduce the blood supply to the tumor through its nutrient artery branches, resulting in the reduction of intraoperative blood loss during removal. Accordingly, the surgical removal of a lesion, which has heavy blood supply, becomes easier with significantly lower surgical risks. Tumors of this class are meningiomas, the paragangliomas, and tumors of the skull and spinal column.